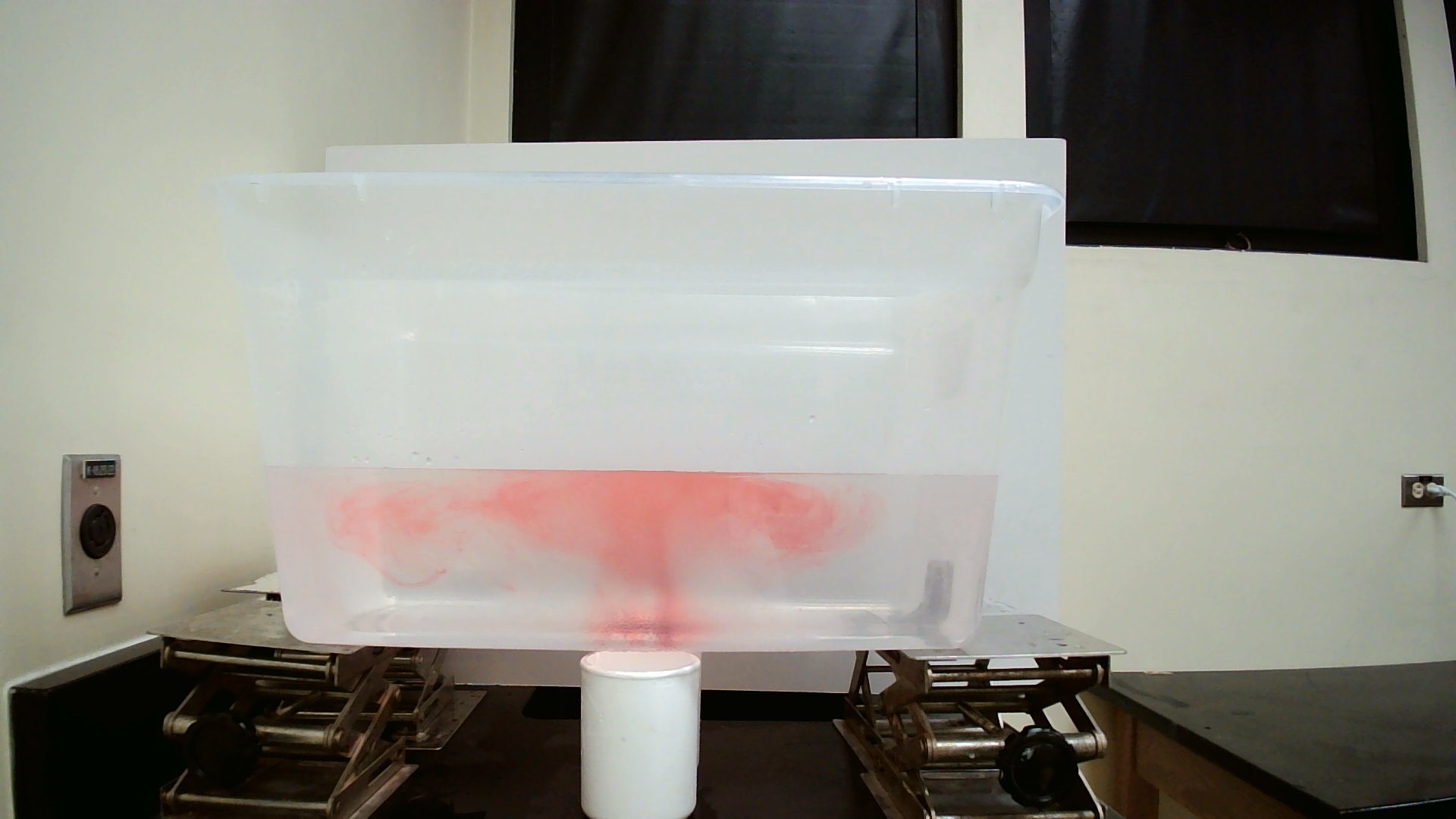
Overview
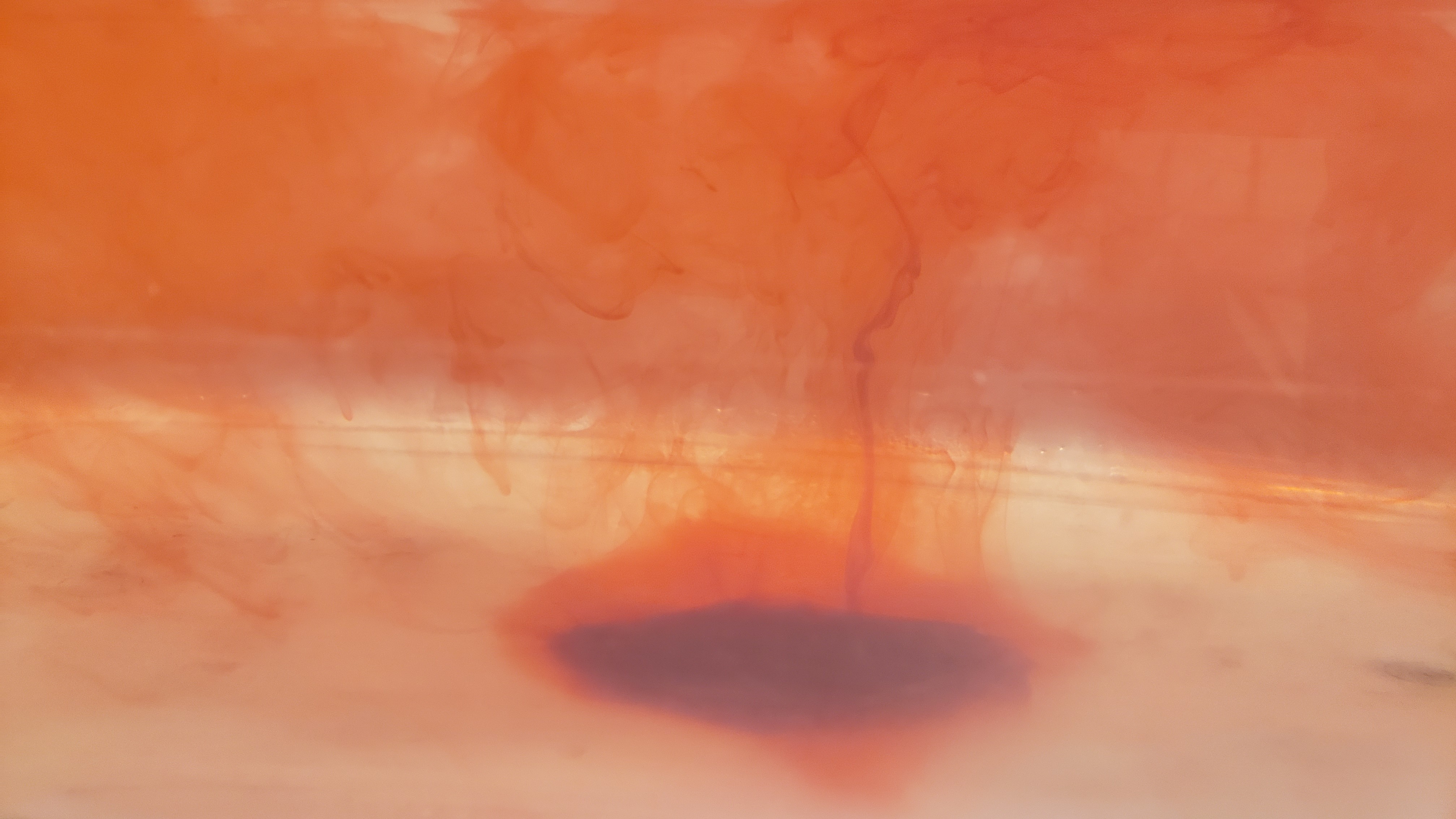
Hurricanes provide a framing for this investigation which focuses on a model of the inside of a hurricane. A convection current is set up in a tank with students making predictions, observations and explanations about the flow. The discussion focuses around how hurricanes forms and where the wind and rain come from. For older students, the strengths and weaknesses of the model as a representation of a hurricane, and the implications for changes in climate are also considered.
- Grades 4-8
- In person and virtual options available.
- For in person visits, access to a water supply and power outlet are required. It is also helpful if books, blocks or similar to prop up the main container can be provided.
- For virtual visits, the Science on the Move staff will set up the tank and manipulate the tank (in real time). Instructions for how to set-up the tank in the classroom can also be shared.
Hurricanes provide a framing for this investigation which focuses on a model of the inside of a hurricane. A convection current is set up in a tank with students making predictions, observations and explanations about the flow. The discussion focuses around how hurricanes forms and where the wind and rain come from. For older students, the strengths and weaknesses of the model as a representation of a hurricane, and the implications for changes in climate are also considered.
- Grades 4-8
- In person and virtual options available.
- For in person visits, access to a water supply and power outlet are required. It is also helpful if books, blocks or similar to prop up the main container can be provided.
- For virtual visits, the Science on the Move staff will set up the tank and manipulate the tank (in real time). Instructions for how to set-up the tank in the classroom can also be shared.
Materials
- Large container or tank
- Jacks or objects to raise container off of surface
- Room temperature water
- Cup of boiling hot water
- Food dye
- Pipette
- Thermal insulating gloves
- Large container or tank
- Jacks or objects to raise container off of surface
- Room temperature water
- Cup of boiling hot water
- Food dye
- Pipette
- Thermal insulating gloves
Follow Up and Resources
This can be an effective launch point for discussion of other topics such as density currents or the links between climate and the ocean. Check out the following
-
Our density currents investigation, Sea for Yourself, framed around ocean currents.
-
NOAA video on hurricane formation. Compare and contrast with the NOAA video on thunderstorm formation.
-
NOAA Hurricanes Education for lesson plans, videos and more.
-
NHC outreach for webinars, simulations and more.
This can be an effective launch point for discussion of other topics such as density currents or the links between climate and the ocean. Check out the following
-
Our density currents investigation, Sea for Yourself, framed around ocean currents.
-
NOAA video on hurricane formation. Compare and contrast with the NOAA video on thunderstorm formation.
-
NOAA Hurricanes Education for lesson plans, videos and more.
-
NHC outreach for webinars, simulations and more.
Standards
Energy Transfer and Transformations
- SC.7.P.11.4: Observe and describe that heat flows in predictable ways, moving from warmer objects to cooler ones until they reach the same temperature.
Earth Structures
- SC.6.E.7.3: Describe how global patterns such as the jet stream and ocean currents influence local weather in measurable terms such as temperature, air pressure, wind direction and speed, and humidity and precipitation.
The Practice of Science
- SC.4.N.1.1: Raise questions about the natural world, use appropriate reference materials that support understanding to obtain information (identifying the source), conduct both individual and team investigations through free exploration and systematic investigations, and generate appropriate explanations based on those explorations.
- SC.5.N.1.1: Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring the identification of variables, collecting and organizing data, interpreting data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
The Role of Theories, Laws and Hypothesis
- SC.4.N.3.1: Explain that models can be three dimensional, two dimensional, an explanation in your mind, or a computer model.
- SC.6.N.3.4: Identify the role of models in the context of the sixth grade science benchmarks.
- SC.7.N.3.2: Identify the benefits and limitations of the use of scientific models.
Energy Transfer and Transformations
- SC.7.P.11.4: Observe and describe that heat flows in predictable ways, moving from warmer objects to cooler ones until they reach the same temperature.
Earth Structures
- SC.6.E.7.3: Describe how global patterns such as the jet stream and ocean currents influence local weather in measurable terms such as temperature, air pressure, wind direction and speed, and humidity and precipitation.
The Practice of Science
- SC.4.N.1.1: Raise questions about the natural world, use appropriate reference materials that support understanding to obtain information (identifying the source), conduct both individual and team investigations through free exploration and systematic investigations, and generate appropriate explanations based on those explorations.
- SC.5.N.1.1: Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring the identification of variables, collecting and organizing data, interpreting data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
The Role of Theories, Laws and Hypothesis
- SC.4.N.3.1: Explain that models can be three dimensional, two dimensional, an explanation in your mind, or a computer model.
- SC.6.N.3.4: Identify the role of models in the context of the sixth grade science benchmarks.
- SC.7.N.3.2: Identify the benefits and limitations of the use of scientific models.