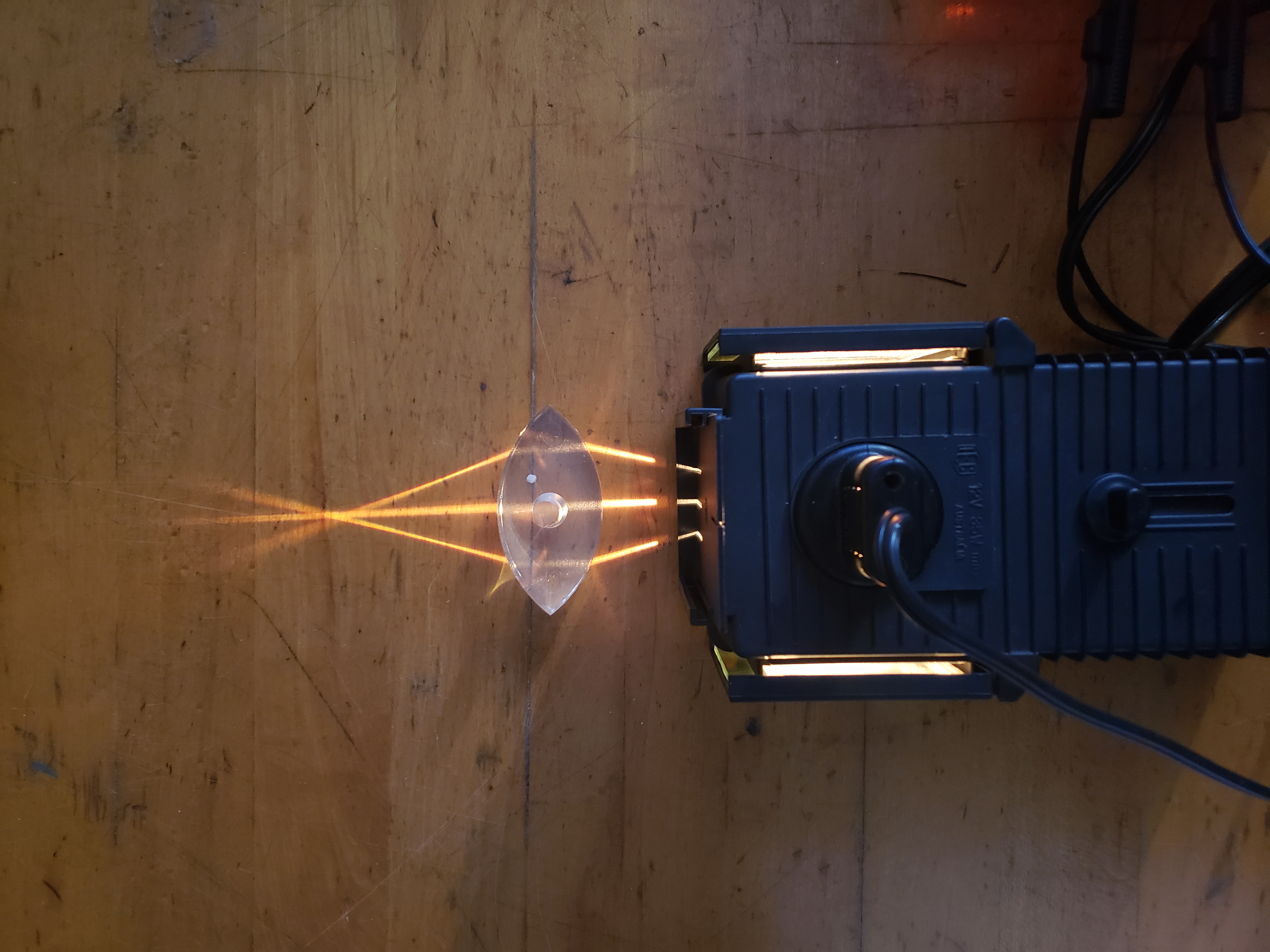
Overview
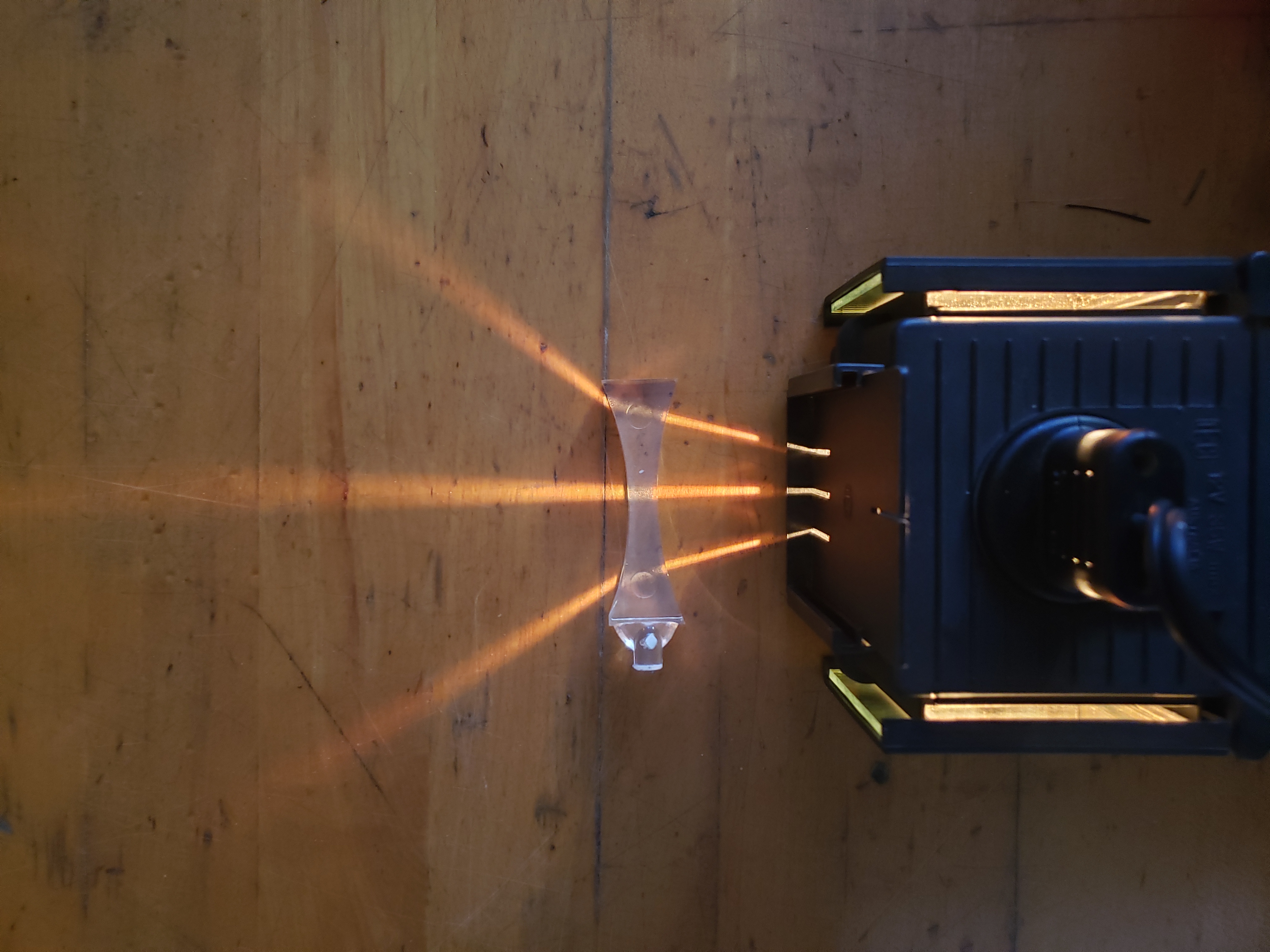
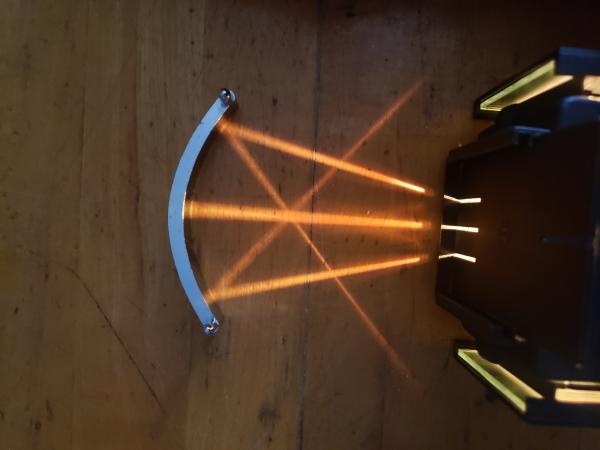
Students make predictions about the path light rays will take when they meet lenses and mirrors of different shapes. Each lens and mirror configuration is set-up by they students and they record observations of the light ray paths. The students then consider which lens shapes result in convergence and which result in divergence. Finally, the investigation closes with consideration of the implications for near- and far-sightedness.
- Grades 4-12
- In person only
- Access to power outlets is required.
Students make predictions about the path light rays will take when they meet lenses and mirrors of different shapes. Each lens and mirror configuration is set-up by they students and they record observations of the light ray paths. The students then consider which lens shapes result in convergence and which result in divergence. Finally, the investigation closes with consideration of the implications for near- and far-sightedness.
- Grades 4-12
- In person only
- Access to power outlets is required.
Materials
- Mirrors and lenses set
- Light box
- 3-slit filter
- Power supply
- Mirrors and lenses set
- Light box
- 3-slit filter
- Power supply
Follow Up and Resources
This can be an effective launch point to dig deeper into reflection, refraction, and associated topics such as Snell's law. Check out the following interactive simulations for more information.
- Optics Bench from the Physics Classroom
- Bending Light simulation from PhET
This can be an effective launch point to dig deeper into reflection, refraction, and associated topics such as Snell's law. Check out the following interactive simulations for more information.
- Optics Bench from the Physics Classroom
- Bending Light simulation from PhET
Standards
Energy
- SC.3.P.10.3: Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels from one medium to another.
- SC.3.P.10.4: Demonstrate that light can be reflected, refracted, and absorbed.
- SC.7.P.10.2: Observe and explain that light can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed.
- SC.912.P.10.22: Construct ray diagrams and use thin lens and mirror equations to locate the images formed by lenses and mirrors.
The Practice of Science
- SC.4.N.1.1: Raise questions about the natural world, use appropriate reference materials that support understanding to obtain information (identifying the source), conduct both individual and team investigations through free exploration and systematic investigations, and generate appropriate explanations based on those explorations.
- SC.5.N.1.1: Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring the identification of variables, collecting and organizing data, interpreting data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
- SC.6.N.1.1/SC.7.N.1.1/SC.8.N.1.1: Define a problem from the sixth/seventh/eighth grade curriculum, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigation of various types, such as systematic observations or experiments, identify variables, collect and organize data, interpret data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
- SC.912.N.1.1:
- Conduct systematic observations
- Use tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data
Energy
- SC.3.P.10.3: Demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels from one medium to another.
- SC.3.P.10.4: Demonstrate that light can be reflected, refracted, and absorbed.
- SC.7.P.10.2: Observe and explain that light can be reflected, refracted, and/or absorbed.
- SC.912.P.10.22: Construct ray diagrams and use thin lens and mirror equations to locate the images formed by lenses and mirrors.
The Practice of Science
- SC.4.N.1.1: Raise questions about the natural world, use appropriate reference materials that support understanding to obtain information (identifying the source), conduct both individual and team investigations through free exploration and systematic investigations, and generate appropriate explanations based on those explorations.
- SC.5.N.1.1: Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring the identification of variables, collecting and organizing data, interpreting data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
- SC.6.N.1.1/SC.7.N.1.1/SC.8.N.1.1: Define a problem from the sixth/seventh/eighth grade curriculum, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigation of various types, such as systematic observations or experiments, identify variables, collect and organize data, interpret data in charts, tables, and graphics, analyze information, make predictions, and defend conclusions.
- SC.912.N.1.1:
- Conduct systematic observations
- Use tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data